The use of pesticides and other chemical fertilizers are essential elements of contemporary agriculture methods aimed at increasing food output. But the widespread use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers has brought about a number of environmental and health risks. The dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, including their effects on food, water, and the environment, will be covered in this article.
What Are Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides?
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides are two important tools used in modern agriculture to improve crop yield and protect crops from pests and diseases. Chemical fertilizers are substances that are added to soil to provide essential nutrients to crops, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The use of chemical fertilizers has helped farmers to increase crop yields and improve the quality of their crops. However, excessive use of chemical fertilizers can lead to soil degradation and can harm the environment, particularly groundwater and surface water, by polluting them with excess nutrients. Pesticides, on the other hand, are chemicals used to kill or control pests and diseases that can harm crops. Herbicides are a type of pesticide used specifically to control weeds. Pesticides have been instrumental in controlling crop losses due to pests and diseases, but they can also have negative impacts on the environment, including harm to non-target species, contamination of soil and water, and the development of pesticide-resistant pests.
Therefore, it’s important for farmers to use chemical fertilizers and pesticides judiciously and in accordance with best practices and regulations to minimize their impact on the environment and ensure sustainable agriculture.
Explanation of Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides
To increase crop yields and safeguard crops against pests and diseases, chemical fertilizers and pesticides are frequently employed in agriculture. Chemical fertilizers give plants the nutrients they need for growth and development, such as nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. Pesticides, on the other hand, are chemicals that are used to eradicate or control pests and illnesses that can harm crops. Chemical pesticides and fertilizers have a substantial environmental impact even though they have been successful in boosting agricultural output.
The dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants include having the potential to contaminate groundwater and result in eutrophication and algal blooms, among other environmental issues. Pesticides can stay in the environment for a very long period and can be dangerous to non-target animals including birds, bees, and other helpful insects.
On the other hand, organic farming practices rely on organic means of fertilization and pest management, such as compost and other organic matter for plant nutrition and natural predators for insect management. Some of the benefits of using organic pest control methods in your garden include that it uses less toxic chemicals and protects the health of the soil.
Commonly Used Types and Examples
Some of the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants have been seen in the following:
- Agricultural hazards are dangers that could befall crops, cattle, and other resources because of a variety of circumstances, including disease outbreaks, climatic conditions, and natural catastrophes. For instance, a drought can reduce crop yields and have an effect on the food supply.
- Threats to the accessibility, quality, and availability of water resources are referred to as “water risks,” and they can have a substantial impact on the environment and on public health. For instance, polluting water supplies can result in sicknesses and disease outbreaks, whilst a lack of water might generate conflict and eviction.
- Environmental dangers include things like air pollution, deforestation, and oil spills that could threaten the environment and its ecosystems. For instance, the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil leak in the Gulf of Mexico severely damaged wildlife and coastal towns.
- Food risks include dangers to the supply of safe, nutritious, and secure food, such as contamination, spoilage, and loss. For instance, contaminated food might cause an outbreak of a foodborne illness, posing health dangers to individuals who consume it.
- Risks to one’s health include those that could be detrimental to their physical, mental, and social well-being. As an illustration, being exposed to dangerous chemicals and pollutants can result in a variety of health issues, from small diseases to significant chronic conditions.
Effects on the Environment
To protect crops from pests, pesticides are frequently applied in agriculture, but this has a negative impact on the environment. These substances have the potential to contaminate food, water, and soil, posing health concerns to both people and wildlife. The dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants include:
- Food: Pesticides can contaminate the food supply and stay in the environment, either through direct application to crops or through runoff into irrigation water sources. Acute or long-term health consequences of eating contaminated food can include endocrine disruption and an increased risk of some cancers.
- Water: Pesticide contamination of groundwater and surface water can have long-term effects on the health of aquatic ecosystems and the quality of drinking water. Some pesticides can disrupt food systems and are hazardous to aquatic life, including fish and amphibians.
- Soil: Pesticides can linger in the soil for many years, diminishing soil fertility and harming beneficial soil organisms. They can also be absorbed by plants, where they are then transferred to animals that eat them.
- Health Risks: Humans who are exposed to pesticides may experience a variety of health impacts, from skin and eye irritation to more severe conditions like brain damage, endocrine disruption, and several malignancies. Regular users of pesticides, such as farmers and farmworkers, are more likely to be exposed to them and experience negative health impacts.
Damage to Soil Health and Biodiversity
The dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants include their effects on biodiversity and soil health. Intensive agricultural techniques can harm the environment and provide health problems, such as the usage of a lot of water, pesticides, and fertilizers.
A decrease in biodiversity and poor soil health can result from pesticides and fertilizers contaminating the soil and groundwater. Reduced agricultural yields might also result from excessive irrigation and high soil salt levels. Farmers should implement sustainable agricultural techniques that reduce the use of pesticides, preserve water, and support diverse and healthy soil ecosystems in order to protect soil health and biodiversity.
Contamination of Water Sources
Public health and the environment are now seriously concerned about water source contamination due to the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants. Increased concentrations of the deadly heavy metal cadmium have been discovered in water sources, posing a major threat to both human health and the ecosystem:
- Toxicity of Cadmium: When taken in significant amounts, the highly poisonous heavy metal Cadmium can result in major health issues. The kidneys, bones, and other organs may suffer harm as a result of it building up in the body. Chronic exposure to cadmium has been associated with a higher risk of cancer, heart disease, and other illnesses.
- Agriculture-Related Contamination: One of the primary causes of cadmium contamination in water sources is agriculture. The use of pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals in agriculture can cause cadmium to leak into the groundwater and soil. The use of animal waste and sewage sludge as fertilizer on fields can also increase the contamination of fields with cadmium.
- Water Pollution: Cadmium poisoning of water sources can have detrimental effects on human health. Leaching from soil and debris as well as the disposal of industrial and agricultural waste into rivers and lakes are two ways that cadmium can get into the water supply. This may cause drinking water to become contaminated and expose people and wildlife to the deadly metal.
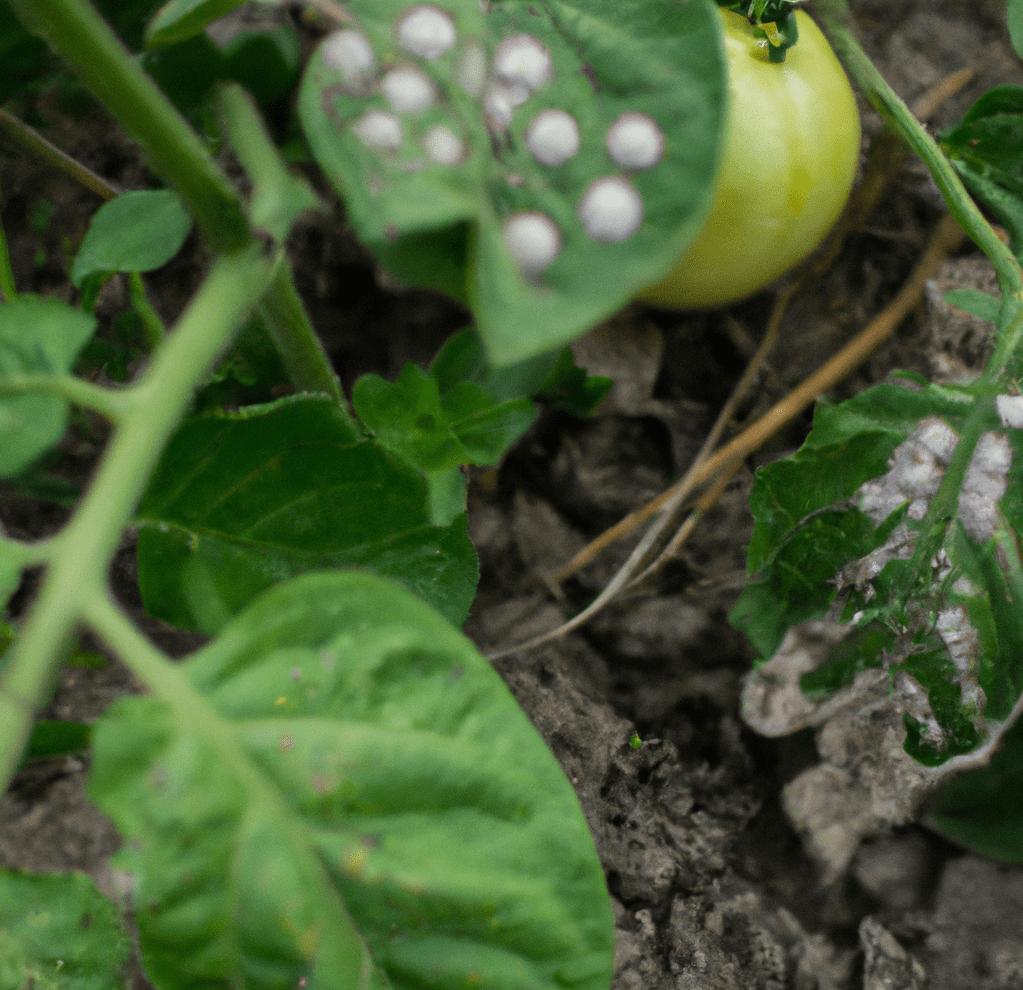

Negative Impact on Pollinators and Other Beneficial Insects
By assisting in the pollination of plants, which contributes to the production of food and the preservation of biodiversity, pollinators and other helpful insects play a critical role in preserving the balance of our ecosystem. These insects have suffered a great deal as a result of human actions like the use of pesticides, habitat damage, and climate change. However, the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, particularly neonicotinoids, affect bee populations. These substances are frequently employed in agriculture, and because they can be absorbed by plants, they make them hazardous to insects that consume them. This might hurt other helpful insects as well as cause a fall in bee populations.
Another important cause of the reduction of pollinators and other helpful insects is habitat deterioration. There is less room for these insects to exist and hunt for food as a result of the loss of natural ecosystems including meadows, woodlands, and wetlands. Their populations may suffer as a result, which will make it harder for them to play their part in the ecosystem.
Finally, pollinators and other helpful insects are also being impacted by climate change. The timing of plant blossoming and the amount of food that is available to these insects can both be impacted by changes in temperature and precipitation patterns. Insect populations may decrease as a result of a mismatch between the insects and the plants they depend on.
Effects on Human Health
The food and water we consume are significantly impacted by agricultural methods, which have a considerable effect on human health. Because of the possible harm to human health, the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants have drawn attention. Pesticides have the ability to pollute both the food and water we consume, which could have negative effects on our health. Numerous health problems, such as headaches, nausea, and neurological disorders, can result from eating food that has been tainted with pesticides.
Long-term pesticide exposure can also raise the risk of some cancers, birth abnormalities, and other chronic illnesses. Similarly, polluting water sources can endanger human health. Pesticides have the potential to contaminate adjacent towns’ drinking water through groundwater seepage. Numerous health issues, including digestive issues, developmental issues, and reproductive issues, may result from this.
Agricultural practices have an impact on human health not only through the food and water we consume but also through additional channels including air pollution and the degradation of natural habitats. Adopting sustainable agriculture techniques that reduce the use of toxic pesticides and safeguard our food and water supplies from contamination is crucial for promoting public health.
Exposure Through Consumption of Treated Crops
In agriculture, pesticides are frequently employed to safeguard crops from weeds, diseases, and pests. However, the usage of these substances may leave residual pesticides in the land, water, and food that humans eat. Consuming pesticide-treated foods can expose people to health concerns for both the environment and themselves. According to studies on the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, long-term exposure to low quantities of pesticides through the intake of food and water can result in a variety of health issues, such as cancer, neurological damage, and endocrine disruption.
The effects of pesticide exposure might be particularly harmful to children and pregnant women. Pesticide-related soil contamination may have an ongoing effect on the environment, harming wildlife and ecosystem health. As a result, crops produced in the same soil may get contaminated, increasing the number of pesticides people are exposed to through their diet.
Possible Links to Certain Cancers and Other Health Issues
According to studies on the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, exposure to pesticides may raise the risk of developing some malignancies, including leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, as well as other health concerns, such as neurological conditions, birth defects, and endocrine disruption.
It’s crucial to remember that the precise mechanisms through which pesticides can result in various health issues are still poorly known. Consequently, additional study is required to demonstrate a direct connection between pesticide exposure and particular health outcomes.
Risks to Farm Workers and Those Living in Close Proximity to Treated Fields
Pesticide exposure is more likely to affect farm workers and residents who live close to treated fields because they may breathe the chemicals in during application or come into touch with them in other ways. Both immediate and long-term health impacts, such as the issues mentioned above, may result from this, including eye and skin irritation, headaches, and nausea.
Alternatives to Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides
The ability to feed the world’s population depends on agricultural productivity, yet the growing use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers has led to worries about their effects on the environment. While chemical fertilizers and pesticides are intended to boost crop yields and protect against pests and diseases, they may also have detrimental impacts on the water supply, wildlife, and public health in addition to increasing crop yields and protecting against pests and diseases.
Fortunately, there are natural alternatives that can be utilized in place of artificial fertilizers and pesticides in agricultural production in light of the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants. Organic farming, which uses natural processes and inputs like compost and cover crops to maintain soil health and encourage plant development, is one alternative. Synthetic pesticides are likewise discouraged in organic agricultural practices, which instead encourage the use of biological controls like beneficial insects and disease-resistant crops.
A different option is to employ integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which combine cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted pesticide applications to limit the need for synthetic pesticides. With less overall usage of synthetic pesticides and the associated environmental dangers, this strategy can help to lessen the effect of pests and diseases on crops.
Organic Farming Practices
Without using synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms, organic farming stresses the use of natural ways to develop crops and raise livestock (GMOs). Unlike the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, organic farming techniques attempt to preserve a balanced soil ecology, lower the danger of soil erosion, and conserve water. Organic farmers contribute to reducing the environmental effect of agriculture and the risk of groundwater pollution by employing natural ways to control pests and illnesses.
Additionally, by encouraging the development of a wide variety of plant and animal species, organic farming techniques also aid in the conservation of biodiversity. Also, organic farming improves the quality and safety of food. Organic food is frequently regarded as being safer and healthier for customers due to the absence of potentially hazardous chemicals. Using organic farming practices results in foods that are more flavorful and nutrient-dense since the natural flavor and nutrients of the food are preserved.
Integrated Pest Management
IPM is a strategy for pest management that places an emphasis on using a variety of tactics to target pests while avoiding harm to people, plants, and the environment. This method seeks to balance effective pest control with limiting unfavorable impacts, acknowledging that complete bug extermination is not always necessary or desirable.
IPM identifies the most efficient management strategies by considering the life cycle, behavior, and environment of the pests. Depending on the particular pest and circumstance, this may require a combination of physical, biological, and chemical control measures. IPM aims to lower insect populations rather than completely eradicate them so that they no longer pose a threat to either plants or people, unlike the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants.
The Use of Cover Crops and Composting
To improve soil health, decrease pesticide use, and increase food production, sustainable agriculture practices like cover crops and composting are crucial. Cover crops, commonly referred to as green manures, are plants produced particularly to enhance soil health. Numerous advantages are offered by them, including decreased soil erosion, enhanced soil structure, increased water infiltration and retention, and weed suppression.
Unlike the dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, cover crops can also increase soil fertility and stimulate the establishment of advantageous soil bacteria, lowering the demand for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides by providing organic matter to the soil. Composting is the process of decomposing organic matter such as food scraps and yard waste to create a rich soil supplement called compost.
Natural fertilizers like compost can enhance soil fertility, water-holding capacity, and structure while lowering the demand for synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Farmers may sustain a healthy soil ecosystem and lower the health hazards connected with pesticide use by amending the soil with compost. Utilizing cover crops and composting, in addition to enhancing soil health, can help reduce water use since healthy soil is better able to hold onto moisture. This can improve food output, lower the risk of soil erosion, and lessen the need for synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. It can also assist to conserve water.
Bottom Line: The Dangers of Using Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides on Edible Plants
The dangers of using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants have raised serious concerns for the environment’s health as well as the health of human consumers. Alternatives that are safer and more environmentally friendly must be taken into account because these chemicals have a substantial impact on the quality of food, water, and soil.
Both the environment and human health can be harmed by using chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Particularly pesticides have been connected to a wide range of health issues, including cancer, neurological impairment, and birth defects. They may also taint water supplies and upset the harmony of ecosystems. While chemical fertilizers may boost yields temporarily, they can also cause long-term soil deterioration and fertility decrease.
Chemical pesticides and fertilizers should not be used indefinitely because they are not only hazardous but also unsustainable. It’s essential to move toward safer and more sustainable farming practices in order to save the environment and human health.
The Dangers of Using Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides on Edible PLants FAQs
What are pesticides and chemical fertilizers?
Chemical fertilizers are compounds applied to crops to supply plants with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for growth and development. Chemicals known as pesticides are used to prevent pests and diseases from harming crops.
What risks are associated with applying chemical pesticides and fertilizers on edible plants?
Contamination of the land, water, and food supply is a threat to human and animal health. This may disturb the endocrine system, raise the risk of some malignancies, have an adverse effect on aquatic ecosystems, and lower the quality of drinking water. Farmers and farmworkers who regularly use pesticides are more likely to suffer serious health effects. Chemical pesticides and fertilizers can also have a negative impact on soil health and biodiversity.
What effects do chemical pesticides and fertilizers have on the environment?
Pesticide use in agriculture has the potential to harm the environment through contaminating soil, water, and food. Pesticides have a long environmental shelf life, which lowers soil fertility and harms important soil species. Additionally, they can be taken up by plants and passed on to animals that eat them via plants.
How are public health and water sources impacted by the usage of chemical fertilizers and pesticides?
Due to the risks associated with utilizing chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, public health and the environment are increasingly gravely concerned about water source contamination. The ecosystem and human health are both seriously threatened by the rising levels of the heavy metal cadmium in water sources. Regular pesticide exposure may have a range of negative health effects, from skin and eye irritation to more serious illnesses like brain damage, endocrine disruption, and various malignancies.
What are a few advantages of using organic farming methods?
Organic fertilization and pest control techniques, such as compost and other organic matter for plant nourishment and natural predators for bug management, are a key component of organic agricultural practices. This process safeguards soil health while using less hazardous chemicals.
What are a few of the risks related to agricultural risks?
Agricultural hazards are risks that could affect livestock, crops, and other resources due to a variety of events, such as disease outbreaks, extreme weather, and natural disasters. These dangers can affect crop productivity and the availability of food.
What dangers do contaminated waters pose?
Water hazards are dangers to the availability, access, and quality of water resources, which can have a significant effect on the environment and general well-being. For instance, contaminated water sources can cause sickness and disease epidemics, whereas a water shortage could lead to war and displaced people.
What are some of the risks to the environment?
Air pollution, deforestation, and oil spills are examples of environmental hazards that potentially endanger the environment and its ecosystems. These risks have the potential to seriously harm coastal towns and wildlife.
Which hazards are associated with food?
Food risks are threats to the availability of healthy, wholesome food, such as contamination, deterioration, and loss. Foodborne illness outbreaks can be brought on by contaminated food, endangering the health of individuals who consume it.
What health risks are present?
Health risks are those that could be harmful to a person’s physical, mental, or social well-being. For instance, exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants can cause a range of health problems, from minor ailments to significant chronic disorders.
What is organic agriculture?
A technique for growing crops and raising livestock without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms is known as organic farming. It emphasizes the use of natural methods to preserve water and preserve a healthy soil ecosystem.
What advantages can organic farming practices offer?
Environmental protection, lowered danger of groundwater pollution, biodiversity preservation, increased food quality and safety, and the production of more tasty, nutrient-dense meals are just a few advantages of organic farming.
What is IPM?
IPM is a method of managing pests that focuses on employing various methods to target pests while causing the least amount of damage to humans, plants, and the environment. To determine the most effective management techniques, it takes into account the pests’ life cycle, behavior, and environment.
What advantages can IPM offer?
In contrast to the risks associated with using chemical fertilizers and pesticides on edible plants, IPM helps to balance effective pest management with avoiding adverse effects. It is a safer and greener alternative to chemical pesticides because it reduces insect populations rather than attempting to eradicate them.
What do composting and cover crops have to do with sustainable agriculture?
In order to boost food production, reduce pesticide use, and improve soil health, sustainable agriculture practices including cover crops and composting are implemented. Composting is the process of allowing organic matter to break down in order to produce a rich soil amendment, whereas cover crops, usually referred to as green manures, are plants produced particularly to improve soil health.
What advantages do composting and cover crops in agriculture have?
Composting and cover crops can improve soil structure, water-holding capacity, and fertility while reducing the need for synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. They can also increase food production, stop soil erosion, consume less water, and aid with water conservation.







